Bridges
Bridges are complete webhook workflows in Hooklistener that connect Sources (webhook receivers) to one or more Destinations (webhook forwarders). A Bridge defines the entire path a webhook takes from arrival to delivery, including any transformations, filters, and retry logic along the way.
Overview
A Bridge brings together all the components needed for webhook automation:
- Source: Where webhooks are received
- Destinations: Where webhooks are forwarded (one or many)
- Filters: Conditional routing rules
- Transformations: Payload modifications
- Retry logic: Automatic failure recovery
- Circuit breakers: Failure protection
Think of a Bridge as a complete, configurable pipeline for webhook data. When a webhook arrives at the Source, Hooklistener processes it through the Bridge and delivers it to all configured Destinations.
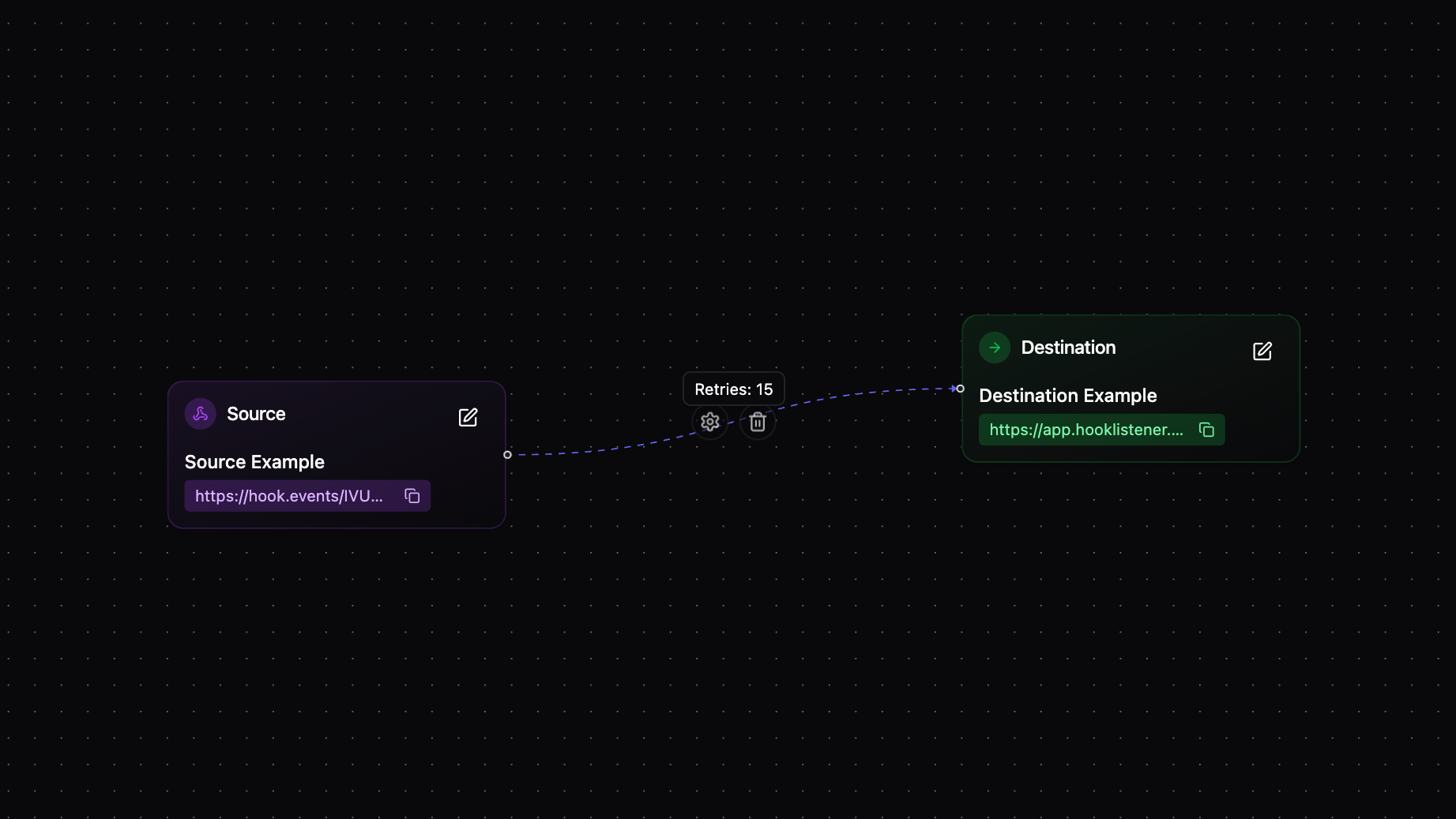
How Bridges Work
Basic Flow
- Webhook arrives at the Source URL
- Authentication is verified (if configured)
- Deduplication checks if this webhook was already processed
- Global filters determine if processing should continue
- For each Destination:
- Destination filters check if this destination should receive the webhook
- Transformation modifies the payload (if configured)
- Delivery attempt sends the webhook to the destination
- Retry logic handles failures automatically
- Circuit breaker protects against cascading failures
Visual Bridge Builder
Hooklistener provides a visual Bridge Builder in the dashboard that lets you:
- Drag and drop components to design your workflow
- See the complete flow from Source to Destinations
- Configure each component inline
- Test the Bridge before deploying
- Monitor execution in real-time
Access the Bridge Builder:
- Navigate to Bridges in the dashboard
- Click "Create Bridge" or edit an existing Bridge
- Use the visual editor to configure your workflow
Creating a Bridge
Via Dashboard (Recommended)
Method 1: Step-by-Step Wizard
- Go to Bridges → "Create Bridge"
- Name your Bridge (e.g., "GitHub to Slack", "Stripe Payments")
- Configure Source:
- Choose existing Source or create new
- Set up authentication if needed
- Add Destinations:
- Select destination type (HTTP, Slack, Discord, etc.)
- Configure endpoint URL
- Add custom headers
- Set retry options
- Optional: Add Filters to route conditionally
- Optional: Add Transformations to modify payloads
- Test the Bridge with sample data
- Activate to start processing webhooks
Method 2: Visual Bridge Builder
- Go to Bridges → "Create Bridge"
- Click "Use Bridge Builder"
- Drag components onto the canvas:
- Start with a Source node
- Add Destination nodes
- Connect with edges (arrows)
- Configure each node by clicking it
- Add filters or transformations to edges
- Save and activate
Via API
curl -X POST https://api.hooklistener.com/api/v1/bridges \
-H "Authorization: Bearer YOUR_API_KEY" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"name": "GitHub to Slack Notifications",
"source": {
"name": "GitHub Events",
"type": "webhook",
"auth_type": "hmac_sha256",
"secret_key": "{{GITHUB_WEBHOOK_SECRET}}"
},
"destinations": [
{
"name": "Slack Alerts Channel",
"type": "slack",
"webhook_url": "{{SLACK_WEBHOOK_URL}}",
"filters": [
{
"body.action": { "$eq": "opened" }
}
]
}
]
}'
Bridge Configuration
Source Configuration
Each Bridge has exactly one Source that receives webhooks:
Basic Settings:
{
"source": {
"name": "Production Events",
"type": "webhook"
}
}
With Authentication:
{
"source": {
"name": "GitHub Repository",
"type": "webhook",
"auth_type": "hmac_sha256",
"secret_header": "X-Hub-Signature-256",
"secret_key": "{{GITHUB_SECRET}}"
}
}
With Deduplication:
{
"source": {
"name": "Payment Events",
"type": "webhook",
"dedup_enabled": true,
"dedup_key": "body.event_id",
"dedup_window": 3600
}
}
See Sources for detailed source configuration.
Destination Configuration
Bridges can have multiple destinations - the same webhook can be forwarded to many endpoints:
Multiple Destinations Example:
{
"destinations": [
{
"name": "Internal API",
"type": "http",
"url": "https://api.company.com/webhooks"
},
{
"name": "Slack Notifications",
"type": "slack",
"webhook_url": "{{SLACK_WEBHOOK_URL}}"
},
{
"name": "Discord Updates",
"type": "discord",
"webhook_url": "{{DISCORD_WEBHOOK_URL}}"
}
]
}
Each destination is processed independently:
- One destination failure doesn't affect others
- Each can have its own filters, transformations, and retry logic
- Circuit breakers protect each destination separately
See Destinations for detailed destination configuration.
Filters
Filters control which webhooks are processed by the Bridge or specific destinations.
Bridge-level Filters (apply to entire Bridge):
{
"name": "Production Events Only",
"filters": [
{
"body.environment": { "$eq": "production" }
}
],
"destinations": [...]
}
Destination-level Filters (apply to specific destination):
{
"destinations": [
{
"name": "High Value Payments",
"type": "http",
"url": "https://api.company.com/high-value",
"filters": [
{
"body.amount": { "$gte": 100000 }
}
]
},
{
"name": "All Payments",
"type": "http",
"url": "https://api.company.com/all-payments"
}
]
}
Filter Operators:
$eq,$neq: Equality$gt,$gte,$lt,$lte: Comparisons$in,$nin: Array membership$contains,$startsWith,$endsWith: String matching$regex: Pattern matching$exist: Field presence$or,$and,$not: Logical operations
See Filters for comprehensive filter documentation.
Transformations
Transformations modify webhook payloads before delivery to destinations.
Inline Transformation:
{
"destinations": [
{
"name": "Formatted Slack Message",
"type": "slack",
"webhook_url": "{{SLACK_WEBHOOK_URL}}",
"transformation": {
"code": "addHandler('transform', async (request) => { return { ...request, body: { text: `New event: ${request.body.type}` } }; });"
}
}
]
}
Reusable Transformation:
{
"destinations": [
{
"name": "API Endpoint",
"type": "http",
"url": "https://api.example.com/webhook",
"transformation_id": "550e8400-e29b-41d4-a716-446655440000"
}
]
}
Transformations enable:
- Format conversion: Adapt payloads for different APIs
- Data enrichment: Add timestamps, metadata, computed fields
- Payload filtering: Remove or redact sensitive data
- Authentication: Inject signatures, tokens, or custom headers
- Conditional logic: Apply transformations based on payload content
See Transformations for detailed guides and examples.
Retry Configuration
Control how failed deliveries are handled:
Per-Destination Retries:
{
"destinations": [
{
"name": "Critical Endpoint",
"type": "http",
"url": "https://critical-api.com/webhook",
"max_retries": 15
},
{
"name": "Best Effort Endpoint",
"type": "http",
"url": "https://optional-api.com/webhook",
"max_retries": 3
}
]
}
Retry Behavior:
- Exponential backoff: Increasing delays between retries
- Automatic: No manual intervention required
- Per-destination: One failure doesn't affect other destinations
- Configurable: 0-15 retries per destination
See Retries for more information.
Bridge Management
Activating and Deactivating
Activate a Bridge to start processing webhooks:
- Webhooks arriving at the Source will be processed
- Deliveries will be attempted to all destinations
- Retries will be triggered on failures
Deactivate a Bridge to temporarily stop processing:
- Webhooks arriving at the Source will be rejected
- No deliveries will be attempted
- Existing retries will be paused (not cancelled)
Use cases for deactivation:
- Maintenance on destination endpoints
- Testing configuration changes safely
- Temporary service outage
- Debugging issues
Editing Bridges
Changes can be made to active Bridges:
Safe to change while active:
- Bridge name and description
- Destination URLs (takes effect immediately)
- Headers and authentication
- Retry counts
- Filters and transformations
Requires caution:
- Source URL changes (update webhook provider)
- Authentication changes (may reject webhooks)
- Deduplication settings (may affect behavior)
Best practice: Test changes on a duplicate Bridge in a development environment first.
Duplicating Bridges
Create a copy of an existing Bridge:
- Go to Bridges → Select Bridge
- Click "Duplicate"
- Modify the duplicate as needed
- Test before activating
Use cases:
- Create development/staging versions
- Test configuration changes safely
- Set up similar workflows quickly
Deleting Bridges
Deleting a Bridge:
- Stops all webhook processing for that Source
- Cancels pending retries
- Preserves event history for audit purposes
- Cannot be undone (but event data remains)
Monitoring Bridges
Bridge Dashboard
View key metrics for each Bridge:
Health Status:
- 🟢 Healthy: All destinations operating normally
- 🟡 Degraded: Some circuit breakers open or high retry rate
- 🔴 Failing: Multiple destinations failing or source errors
Key Metrics:
- Total events received: Webhooks processed
- Successful deliveries: Webhooks delivered successfully
- Failed deliveries: Webhooks that exhausted all retries
- Pending retries: Webhooks awaiting retry attempts
- Average latency: End-to-end processing time
Destination Breakdown:
- Success rate per destination
- Circuit breaker status
- Current retry queue depth
- Error rates and types
Event History
Access complete logs of all webhooks processed by the Bridge:
Incoming Events tab:
- All webhooks received at the Source
- Payload, headers, and metadata
- Authentication results
- Deduplication status
Outgoing Events tab:
- All delivery attempts to destinations
- Request and response details
- Retry attempts and outcomes
- Transformation logs
- Filter evaluation results
Use event history to:
- Debug delivery failures
- Verify transformations are working correctly
- Audit webhook processing
- Understand traffic patterns
- Troubleshoot filters
Alerts and Notifications
Configure alerts for Bridge health issues:
Alert Conditions:
- Circuit breaker opened
- High failure rate (>5%)
- Repeated authentication failures
- Unusual traffic patterns
- Retries exhausted
Notification Channels:
- Slack
- Discord
- Telegram
- Webhook (send to another Bridge!)
Configure notifications to monitor Bridge health and issues.
Best Practices
Design
-
One Bridge per workflow
- Keep Bridges focused on a single use case
- Example: "GitHub PR Notifications" not "All GitHub Events"
-
Use descriptive names
- Include source and purpose: "Stripe Payments → Internal API"
- Specify environment: "Production GitHub → Slack"
-
Separate environments
- Create distinct Bridges for development, staging, production
- Use different Source URLs to avoid cross-contamination
- Test changes in non-production first
Performance
-
Minimize transformations
- Keep transformation code simple and fast
- Avoid heavy computations or large data structures
- Test performance with realistic payloads
-
Use filters effectively
- Filter early to reduce unnecessary processing
- Place most selective filters first
- Use bridge-level filters for common conditions
-
Monitor latency
- Track end-to-end processing time
- Investigate slow destinations
- Optimize transformation code
Reliability
-
Configure retries appropriately
- Use higher retry counts for critical destinations
- Lower counts for non-critical or best-effort deliveries
- Consider destination SLA when setting limits
-
Monitor circuit breakers
- Set up alerts for open circuits
- Investigate root causes quickly
- Don't repeatedly reset without fixing the issue
-
Handle failures gracefully
- Design destination endpoints to be idempotent
- Implement proper error handling
- Log and monitor all failures
Security
-
Protect Source URLs
- Enable signature verification for all production Bridges
- Use strong webhook secrets
- Rotate secrets regularly
-
Secure destination credentials
- Store all tokens and API keys in Hooklistener Secrets
- Use
{{SECRET_NAME}}syntax in configurations - Never hardcode sensitive data
-
Minimize data exposure
- Use transformations to remove sensitive fields
- Filter out unnecessary data
- Audit what data is sent where
Common Patterns
Fan-out Pattern
Send one webhook to multiple destinations:
{
"name": "Payment Event Fan-out",
"source": {...},
"destinations": [
{
"name": "Accounting System",
"type": "http",
"url": "https://accounting.company.com/webhooks"
},
{
"name": "CRM Update",
"type": "http",
"url": "https://crm.company.com/webhooks"
},
{
"name": "Analytics Platform",
"type": "http",
"url": "https://analytics.company.com/webhooks"
},
{
"name": "Slack Notification",
"type": "slack",
"webhook_url": "{{SLACK_WEBHOOK_URL}}"
}
]
}
Conditional Routing
Route webhooks to different destinations based on content:
{
"name": "Priority-Based Routing",
"source": {...},
"destinations": [
{
"name": "High Priority Queue",
"type": "http",
"url": "https://api.company.com/high-priority",
"filters": [
{ "body.priority": { "$eq": "high" } }
]
},
{
"name": "Normal Queue",
"type": "http",
"url": "https://api.company.com/normal",
"filters": [
{ "body.priority": { "$eq": "normal" } }
]
},
{
"name": "All Events Archive",
"type": "http",
"url": "https://archive.company.com/events"
}
]
}
Format Adaptation
Convert webhook formats between incompatible services:
{
"name": "GitHub to Jira",
"source": {
"name": "GitHub Events",
"type": "webhook"
},
"destinations": [
{
"name": "Jira Issue Creation",
"type": "http",
"url": "https://company.atlassian.net/rest/api/2/issue",
"transformation_id": "github-to-jira-transformer",
"filters": [
{ "body.action": { "$eq": "opened" } },
{ "body.issue.labels": { "$contains": "bug" } }
]
}
]
}
Notification Aggregation
Combine multiple notification channels:
{
"name": "Build Status Notifications",
"source": {...},
"destinations": [
{
"name": "Slack #engineering",
"type": "slack",
"webhook_url": "{{SLACK_ENGINEERING_WEBHOOK}}"
},
{
"name": "Discord #builds",
"type": "discord",
"webhook_url": "{{DISCORD_BUILDS_WEBHOOK}}"
},
{
"name": "Telegram Admins",
"type": "telegram",
"bot_token": "{{TELEGRAM_BOT_TOKEN}}",
"chat_id": "{{ADMIN_CHAT_ID}}",
"filters": [
{ "body.status": { "$eq": "failed" } }
]
}
]
}
Troubleshooting
Webhooks Not Being Received
Verify Source URL:
- Check the URL in your webhook provider matches exactly
- Ensure HTTPS (not HTTP)
- Include any path segments if configured
Check Bridge Status:
- Confirm Bridge is activated
- Review authentication settings
- Check for deduplication issues
Review Event Logs:
- Check incoming events tab for rejected webhooks
- Look for authentication failures
- Verify payload format
Deliveries Failing
Check destination endpoint:
- Verify URL is correct and accessible
- Test endpoint independently
- Review required headers and authentication
Review delivery attempts:
- Check response status codes and error messages
- Look for patterns in failures
- Verify transformation isn't causing errors
Check circuit breaker status:
- If open, wait for automatic recovery or reset manually
- Investigate underlying destination issues
- Monitor recovery attempts
Filters Not Working
Test filter syntax:
- Use the filter test endpoint
- Verify field paths are correct (body.field.nested)
- Check operator usage ($eq, $gt, etc.)
Review event payload:
- Confirm expected fields exist
- Check data types match filter expectations
- Verify array vs object structure
Check filter placement:
- Bridge-level filters apply to all destinations
- Destination-level filters apply only to that destination
- Order matters for complex logic
Transformations Failing
Check syntax errors:
- Validate JavaScript code
- Ensure proper return statements
- Check for missing brackets or semicolons
Review runtime errors:
- Check transformation logs for error messages
- Verify assumptions about payload structure
- Test with actual webhook payloads
Monitor performance:
- Check for timeout errors
- Simplify complex transformations
- Reduce data processing
Next Steps
Now that you understand Bridges, explore related features:
- Configure Filters for conditional routing
- Use Transformations to modify payloads
- Monitor Circuit Breakers for reliability
- Track Issues to resolve problems
- Understand Events to monitor webhook traffic
Bridges are the core of Hooklistener's webhook automation platform. By combining Sources, Destinations, Filters, and Transformations into complete workflows, you can build sophisticated webhook integrations that are reliable, secure, and easy to manage.